MySQL
In this guide, we introduce some knowledge about MySQL database engine. Some knowledge may be specific to the implementation of MySQL, and not applicable to other SQL engines.
Differences between MySQL engines - MyISAM vs InnoDB
- In production, you should almost always use InnoDB rather than MyISAM.
- Starting from MySQL 5.5.5, InnoDB is the default engine for MySQL server.
- InnoDB supports both row-level locking and table-level locking. However, MyISAM only supports table-level locking.
- InnoDB supports transaction management, while MyISAM does not.
- InnoDB supports foreign key, while MyISAM does not.
- InnoDB uses clustered index, while MyISAM uses non-clustered index.
- InnoDB does not store the number of rows in system catalog, while MyISAM does.
- Thus, if you run
SELECT COUNT(*) FROM my_tbl, the query will be much faster on MyISAM.
- Thus, if you run
- InnoDB supports disaster recovery much better than MyISAM.
- InnoDB requies every table to have a primary key. This is because InnoDB is an index-organized storage engine (i.e., it always uses clustered index). InnoDB indeed stores the actual data in the leaf nodes of a B+ tree index for the primary key.
- Thus, it is wise to keep the size of the primary key small.
- If not supplied, an implicit primary key (i.e., a counter of 6 bytes) will be created.
- Searches on secondary index will eventually result in a search on the primary key index.
- InnoDB adds the following columns implicitly to every table:
DB_TRX_ID: the ID of the transaction which last modified this record;DB_ROLL_PTR: a pointer to the previous version of this record (which may be stored in undo log), which would be useful during rollback;DB_ROW_ID: an auto-increment ID which could serve as the primary key if there is no explicit one;DELETED_BIT: a flag for soft-delete of this record, while actual removal would be done by a purge worker asynchronously.
MySQL Index
- Differences between binary tree and B tree:
- B tree is a an n-ary tree, meaning each node could have up to n children rather than 2 children only. This is due to the nature of hard disk where data are stored in per block manner. Using the n-ary tree could reduce the height of the tree.
- Differences between B tree and B+ tree:
- B+ tree only stores actual data in leaf nodes, not internal nodes. This makes each internal node able to contain references to more child nodes. Thus, it further reduces the height of the tree.
- B+ tree maintains a linked list at the leaf level, so that each leaf node contains a pointer to the next leaf node. This is useful for range queries.
- Differences between clustered index and non-clustered index:
- At leaf node level, clustered index stores data within the leaf nodes while non-clusterd index stores a pointer to the data within leaf nodes.
- In InnoDB, primary key is alway a clustered index while other keys would always be non-clustered index.
- Differences between singular index and composite index:
- There are 3 solutions to use B+ tree to represent composite index: 1) store hash table at each leaf node; 2) store inner B+ tree at each leaf node; 3) concatenate all columns together and use it as the key for B+ tree.
- For composite index, the left-most prefix matching principle works when deciding whether a query is covered by an index.
MySQL Character Set
- In production, always use
utf8mb4as the character set for all tables.- Starting from MySQL 8.0,
utf8mb4is the default character set.
- Starting from MySQL 8.0,
utf8character set is not really UTF8-compatible. It uses a maximum of 3 bytes per character.
MySQL Concurrency, Transaction & Isolation Level
- SQL supports 4 fundamental properties: ACID (atomicity, consistency, isolation, durability).
- To ensure the atomicity and durability of a sequence of SQL statements, they have to be wrapped into an SQL transaction.
- However, code without transaction would in general lead to better concurrency performance. We can avoid the use of transaction by careful design.
- Each singlular statement in InnoDB is wrapped inside a transaction, to make it atomic in an intuitive way.
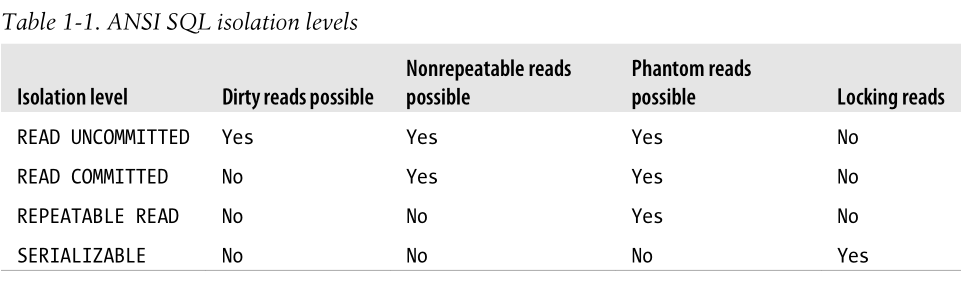
- There are 3 typical issues which is related to isolation:
- Dirty read: a query could read non-committed change, which is dangerous since the change could be rolled back later.
- Non-repeatable read: two queries within the same transaction read different values of the same record.
- Phantom read: a query could not see the update brought by a previous query in the same transaction because some other transaction has modified it.
- According to ANSI SQL standard, there are 4 isolation levels:
- InnoDB by default uses the Repeatable Read isolation level.
- In general, there are 2 ways to achieve isolation: lock-based concurrency control and multi-version concurrency control.
- Most modern database engines such as InnoDB adopt MVCC due to its better performance.
MySQL High Performance & High Availability
- To ensure the high performance of MySQL servers, there are a few aspects to consider:
- Separate read and write: use slaves as read replica;
- Use shard to partition the database;
- Avoid the use of lock and transaction.
- To ensure the high availablity of MySQL servers, we have to:
- Set up a slave for every production MySQL server and the slave must be at a different geographic location;
- Perform daily snapshot-based backup from the slave.
- MVCC (multi-version concurrency control) is useful for applications with high concurrency.
- It is different from the traditional lock-based concurrency control.
- The most classical use case for MVCC is the bank transfer problem.
MySQL Logs
- Primarily, MySQL uses 3 types of logging files to achieve ACID:
- The binlog is a linear history of writes to the database, which can be used for replication purpose. For example, a slave instance will read binlog to follow its master.
- Transaction log is used for rollback and disaster recovery. It is also known as redo log in the old Oracle days. It is basically a technique called WAL (write-ahead logging). When updating transaction log, InnoDB follows an approach of prepare + commit (which is essentially 2PC) to ensure consistency between binlog and transaction log.
- Undo log stores the pre-image of each operation, in order to assist transaction rollback and MVCC.
- In addition, MySQL has the following types of logging files:
- Relay log is stored on the slave instance as a result of the replicationn of master instance’s binlog, so that the master does not have to wait for the slave to finish execution.