We all know that DBMS (database management system) is used to store (a massive amount of) data. However, have you ever wondered how is data stored in DBMS? In this post, we will focus on data storage in RDBMS, the most traditional relational database systems.
Physical Storage
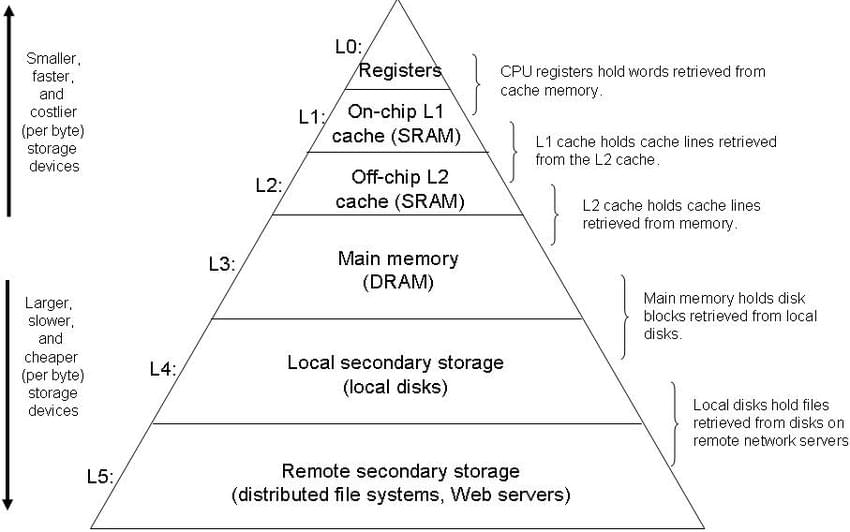
Data can be stored in many different kinds of medium or devices, from the fastest but costy registers to the slow but cheap hard drives, or even magnetic tapes. Nowadays, IaaS providers such as AWS even provides services such as S3 Glacier as a low-cost archiving storage solution. The diagram below shows the memory hierarchy of common devices.