Simple Storage Service (S3)
- S3 is object-based storage, it allows you to store files (up to 5TB) in buckets.
- S3 bucket has a universal namespace. Each bucket name has to be unqiue in its availablity zone (AZ).
- S3 bucket name has to be beween 3 and 63 characters long;
- S3 bucket name can only contain lower-case letters, numbers, dots and dashes;
- S3 bucket name must start with a lower-case letter or number.
- S3 returns HTTP code
200if file is uploaded sucessfully. - Each object stored in S3 consists of
- Key (i.e., file name)
- Value (i.e., file content)
- Version ID
- Metadata
- Access control list (ACL)
- Torrent
- S3 ensures read-after-write consistency for
POSTrequests (i.e., to add new files although AWS calls them newPUTs), while it only guarantees eventual consistency forPUTandDELETErequests.- If you use cross-region replication for your S3 buckets, the changes may not be reflected until the operation is fully propagated to all replicas.
- It is possible to enable MFA for
DELETErequests. - It is also possible to turn on server access logging.
- The log can be sent to another bucket belonging to the same or a different account.
- The pricing model of S3 is calculated based on the storage size + data transfer cost.
- The price for the storage size is different for different tiers;
- The price for data transfer:
- Data transfer into S3 is generally free (although
PUT,POST,HEADrequests do carry a small cost); - Data transfer out of S3 is charged when you go beyond the free tier;
- Data transfer from S3 to CloudFront is currently free;
- Data transfer between S3 and EC2 (within the same region) is currently free.
- Data transfer into S3 is generally free (although
- By default, you can only create up to 100 buckets per AWS account.
- But you can increase this limit to 1000 by submitting a service limit increase.
- When an S3 bucket is used for static website hosting, it is possible to redirect requests for an object to another object in the same bucket or an external URL.
- AWS used to request S3 customers to have randomized prefixes for object names to achieve faster performance (for better sharding). However, this is not the case any more since July 2018.
S3 Tiering
There are different tiers of S3 buckets and the comparison between them is presented in the table below:
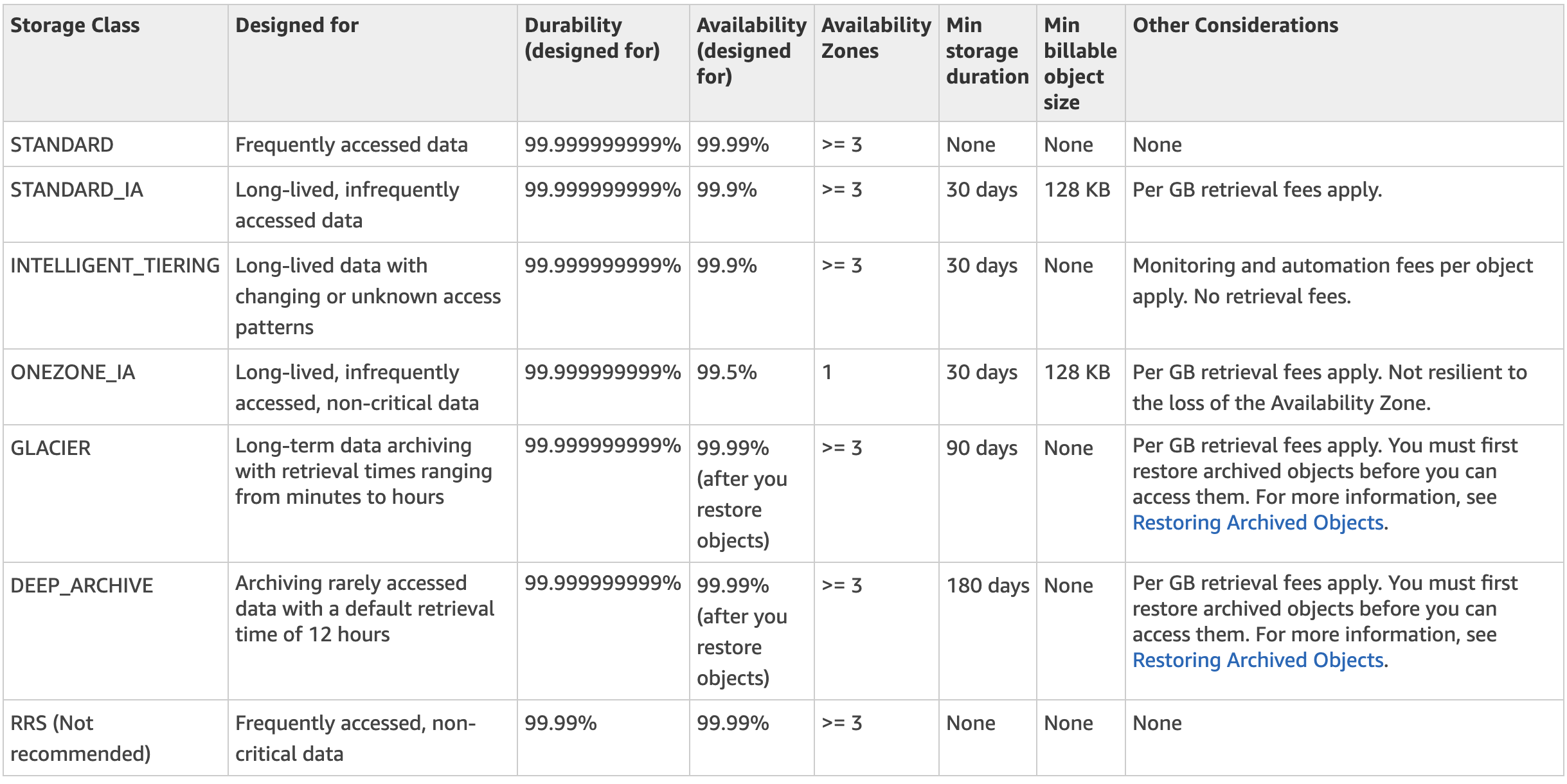
- Compared with S3 Standard class, S3 IA and S3 One-zone IA offers the same durability of 99.999999999%.
- S3 IA and S3 One-zone IA offers the same high-throughput and low-latency feature as S3 Standard;
- Being less frequently accessed does not mean the access for them would be slower. The only tradeoff is an additional retrieval fee;
- S3 IA and S3 One-zone IA requires each object to have a minimum size of 128KB. Objects will still be treated (and charged) as 128KB if smaller than 128KB.
- Compare with S3 Standard and S3 IA class, S3 One-zone IA offers a slightly lower availability of 99.5%.
- Compared with S3 Standard class, S3 Reduced Redundancy Storage (RRS) offers a much lowwer durability of 99.99%, but offers the same availablity of 99.99%.
- It is not recommended to use S3 RRS for new projects in some regions.
- Usually, the first-byte latency for S3 Glacier would be 3 - 5 hours. However, AWS does provide different retrieval options, from a few minutes to hours:
- Expedited retrieval: access data in 1 - 5 minutes, for occasional urgent requests to retrieve a subset of archives, costing $0.03 per GB retrieved;
- Standard retrieval: access data in 3 - 5 hours, costing $0.01 per GB retrieved;
- Bulk retrieval: access large amount of data in 5 - 12 hours, costing $0.0025 per GB retrieved.
- The first-byte latency for S3 Glacier Deep Archive would be within 12 hours.
Security & Encryption
- Access control to an S3 bucket can be managed using either a bucket ACL or a bucket policy.
- By default, all newly created buckets are private.
- There are 3 approaches to achieve encryption for your interaction with S3 buckets:
- Encryption in transit: using SSL/TLS (or HTTPS);
- Server-side encryption (encryption at rest): the key could be from
- S3 managed keys (also known as SSE-S3); or
- AWS key management service (also known as SSE-KMS); or
- Customer provided keys (also known as SSE-C);
- Client-side encryption: the data would be encrypted before sent out.
Versioning & Lifecycle
- Using versioning with S3 could be used to backup data (similar to any VCS).
- It stores all versions of an object (all writes + delete marker).
- Once enabled, versioning cannot be disabled. It can only be suspended.
- Versioning can be integrated to lifecycle rules to optimize the size of the data stored.
- Similar to the eviction policy (such as LFU or LRU) for Redis cache.
- MFA delete can only be used when versioning is enabled.
- If a bucket's versioning configuration is MFA Delete–enabled, the bucket owner must include the
x-amz-mfaheader in requests to permanently delete an object version or change the versioning state of the bucket; - All authorized IAM users can enable versioning, but only the bucket owner can enable MFA Delete.
- If a bucket's versioning configuration is MFA Delete–enabled, the bucket owner must include the
- Lifecycle automates moving your objects between different storage classes.
- It can be used in conjuction with versioning;
- It can be applied to current version and/or previous versions.
Replication & Acceleration
- If you turn on cross-region replication, changes to objects in one bucket will be automatically propagated to another bucket for faster retrieval & disaster recovery purposes.
- Replication can be done for the whole bucket or object-based with certain prefixes or tags only;
- Versioning must be enabled on both source bucket and destination bucket;
- Files which are existing in a bucket when replication is turned on are not replicated automatically. However, subsequent updates to these files would be replicated;
- Delete markers are not replicated;
- Deletion of individual versions or delete markers (manually) would not be replicated;
- Cross-region replication does not support chaining. In other words, it will not work if the source bucket is replicated from another bucket.
- It is also impossible to cross-region replicate buckets encrypted with SSE-C.
- Transfer acceleration takes advantage of CloudFront. Data arrived at edge locations will be routed to S3 over an optimized network path.