Elastic Block Store (EBS)
- Each EBS volume is automatically replicated within its AZ for HA and durability.
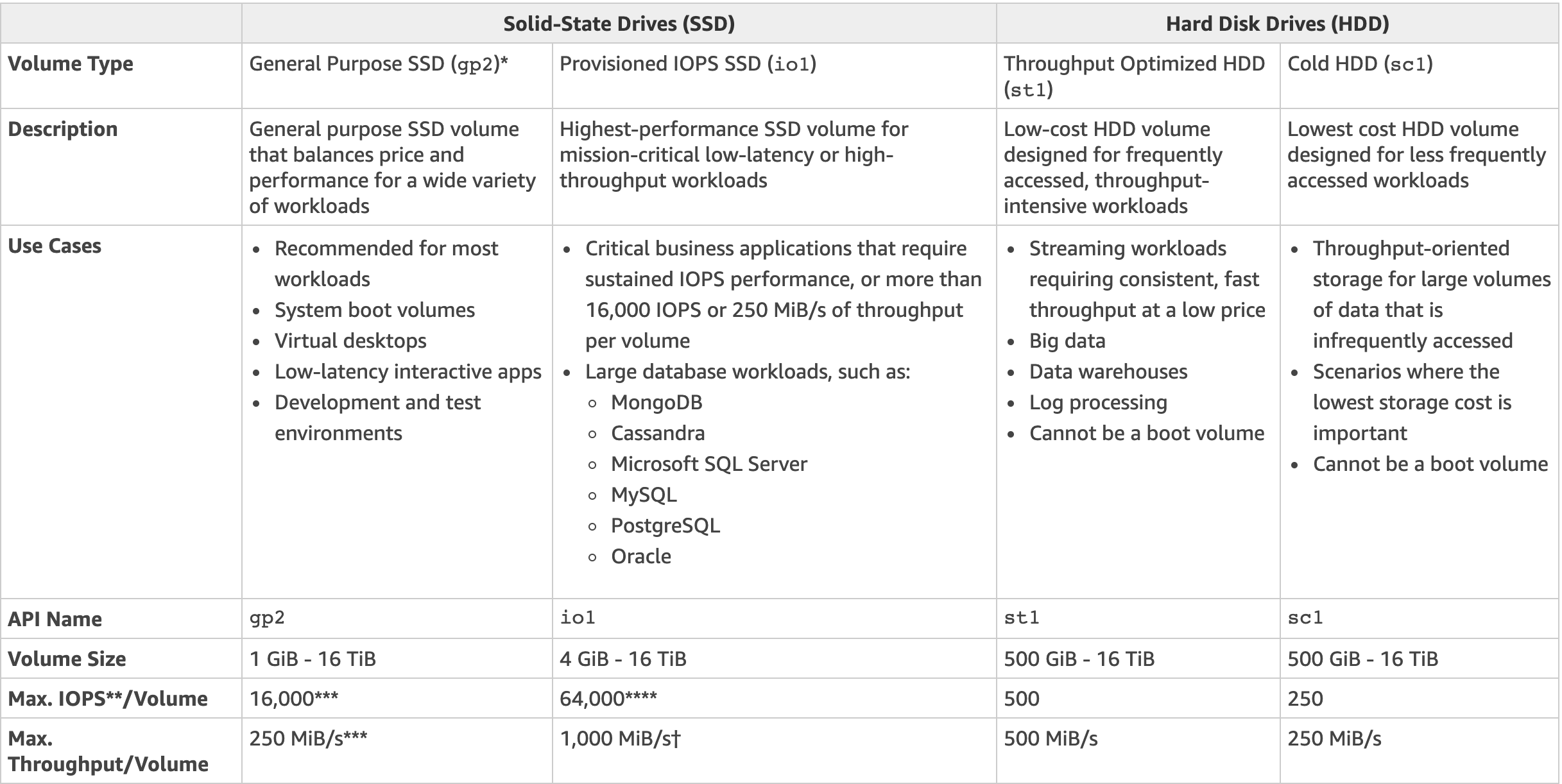
- There are 5 different types of EBS storage:
Volumes & Snapshots
- For an EBS-backed EC2 instance, the EBS volume and EC2 instance must be in the same AZ.
- The root EBS of an EC2 instance will be deleted by default when the instance is terminated.
- Snapshots exist on S3. They are point-in-time copies of volumes.
- To take a snapshot of an EBS volume, it has to go through 2 phases: initial cataloguing phase (lock the file system and calculate the change list, during which the volume cannot be accessed) and data copying phase (copy the changes to S3).
- Snapshots are also incremental (only blocks that have changed since last snapshot will be moved to S3).
- Thus, it will take some time to create the 1st snapshot (because the whole volume need to be copied).
- If you want to create a snapshot for a root volume of a production EC2 instance, it is better to deregister that instance from ELB and then terminate it.
- This could give you a consistent state of the snapshot (as the OS may continuously write to the root volume);
- This could also avoid potential performance degrade caused by writing snapshot (because the volume will be unavailable during the initial cataloguing phase).
- AMIs can be created from both volumes and snapshots.
- To migrate one EC2 instance to another AZ in the same region:
- Take a snapshot of the EBS volume;
- Create an AMI from the snapshot;
- Use the created AMI to launch a new EC2 instance in the destination AZ.
- To migrate one EC2 instance to another region:
- Take a snapshot of the EBS volume;
- Create an AMI from the snapshot;
- Copy the created AMI to the destination region;
- Use the copied AMI in the destination region to launch a new EC2 instance.
Amazon Machine Image (AMI)
- When using AMIs, they could be backed by 2 types of devices:
- EBS volumes: created from an EBS snapshot;
- Instance store: created from an instance store volume using a template stored on S3.
- Instance store backed volumes are sometimes called ephemeral volumes.
- They cannot be stopped. Data will be lost if you try to stop them;
- If the underlying host fails, data will be lost;
- They can be rebooted and data won't be lost.
- EBS backed volumes can be stopped and rebooted. Data won't be lost.
- By default, root volumes of both types will be deleted on termination.
- For EBS backed volumes, it can be configured to not delete root volume when terminated.
Encryption
- Root volumes cannot be encrypted by default at creation time.
- However, you can encrypt it when you copy the snapshot created from it.
- Snapshots of encrypted volumes are encrypted automatically.
- Volumes restored from encrypted snapshots are also encrypted automatically.
- Snapshots can be shared only if they are unencrypted.